北风推荐引擎
最近,我被要求提出一种提供推荐的方法。幸运的是,通过在最近的Neo4j伦敦聚会上从Max De Marzi和Mark Needham的演讲中获得的知识,我知道这可以很容易地通过Neo4j实现。
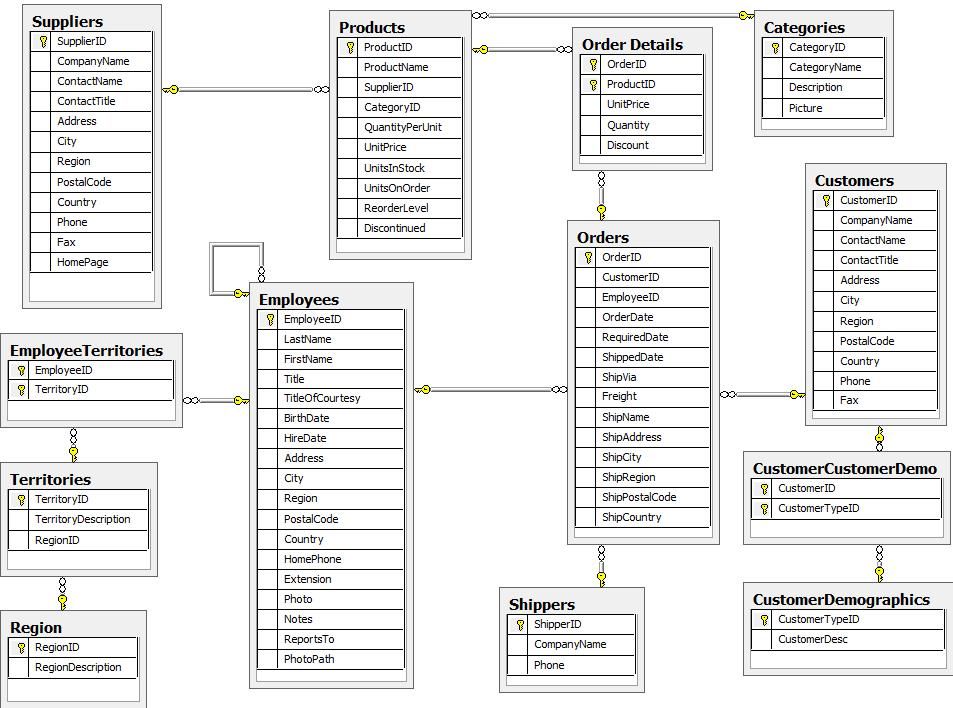
推荐引擎的关键问题在于数据。幸运的是,Neo4j捆绑了Northwind图示例。Northwind数据库是一个著名的包含购买历史的数据集,多年来一直用于教授关系数据库,是开始的好地方。
您可以通过遵循Neo4j上“将数据导入Neo4j”的帖子,将Northwind数据库导入图谱中,或者在Neo4j的浏览器中输入以下内容,例如Neo4j Desktop中的空数据库或空白沙盒。
:play northwind graph
以下是手动加载数据的方法
现在我们有了一些数据,让我们开始探索这个数据集。
热门产品
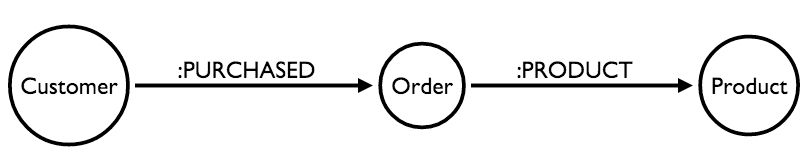
为了找到数据集中最受欢迎的产品,我们可以追踪从:Customer到:Product的路径
match (c:Customer)-[:PURCHASED]->(o:Order)-[:PRODUCT]->(p:Product)
return c.companyName, p.productName, count(o) as orders
order by orders desc
limit 5基于内容的推荐
我们能为客户做出的最简单的推荐是基于内容的推荐。根据他们之前的购买记录,我们能否向他们推荐任何他们尚未购买的商品?对于我们的客户购买的每件产品,让我们看看其他客户还购买了什么。每个:Product都与一个:Category相关联,因此我们可以用它来进一步缩小推荐产品列表。
match (c:Customer)-[:PURCHASED]->(o:Order)-[:PRODUCT]->(p:Product)
<-[:PRODUCT]-(o2:Order)-[:PRODUCT]->(p2:Product)-[:PART_OF]->(:Category)<-[:PART_OF]-(p)
WHERE c.customerID = 'ANTON' and NOT( (c)-[:PURCHASED]->(:Order)-[:PRODUCT]->(p2) )
return c.companyName, p.productName as has_purchased, p2.productName as has_also_purchased, count(DISTINCT o2) as occurrences
order by occurrences desc
limit 5目前为止相当标准。
协同过滤
协同过滤是推荐引擎使用的一种技术,它根据其他客户的反馈来推荐内容。为此,我们可以使用k-NN(k最近邻)算法。k-NN通过根据项目彼此之间的相似性将它们分组进行分类。在我们的案例中,这可能是两个客户对某个产品的评分。举一个现实世界的例子,Netflix等网站就是通过这种方式,根据你已经看过的节目的评分来提供推荐的。
要使这个模型起作用,我们首先需要创建一些“评分关系”。目前,让我们根据客户购买产品的次数,为每个产品创建一个介于0到1之间的分数。
MATCH (c:Customer)-[:PURCHASED]->(o:Order)-[:PRODUCT]->(p:Product)
WITH c, count(p) as total
MATCH (c)-[:PURCHASED]->(o:Order)-[:PRODUCT]->(p:Product)
WITH c, total,p, count(o)*1.0 as orders
MERGE (c)-[rated:RATED]->(p)
ON CREATE SET rated.rating = orders/total
ON MATCH SET rated.rating = orders/total
WITH c.companyName as company, p.productName as product, orders, total, rated.rating as rating
ORDER BY rating DESC
RETURN company, product, orders, total, rating LIMIT 10现在我们的模型应该看起来像这样
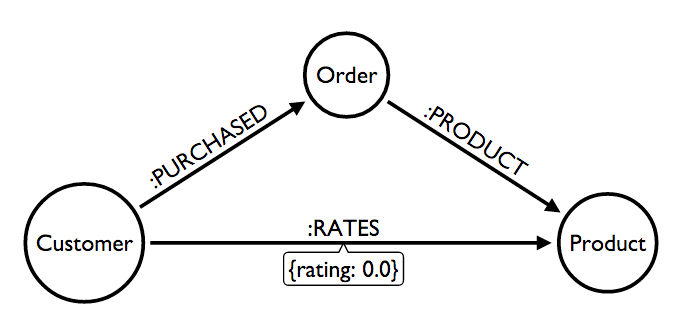
MATCH (me:Customer)-[r:RATED]->(p:Product)
WHERE me.customerID = 'ANTON'
RETURN p.productName, r.rating limit 10现在我们可以使用这些评分来比较两位客户的偏好。
// See Customer's Similar Ratings to Others
MATCH (c1:Customer {customerID:'ANTON'})-[r1:RATED]->(p:Product)<-[r2:RATED]-(c2:Customer)
RETURN c1.customerID, c2.customerID, p.productName, r1.rating, r2.rating,
CASE WHEN r1.rating-r2.rating < 0 THEN -(r1.rating-r2.rating) ELSE r1.rating-r2.rating END as difference
ORDER BY difference ASC
LIMIT 15现在,我们可以使用余弦相似度在两位客户之间创建相似性分数(感谢Nicole White提供的原始Cypher查询…)
MATCH (c1:Customer)-[r1:RATED]->(p:Product)<-[r2:RATED]-(c2:Customer)
WITH
SUM(r1.rating*r2.rating) as dot_product,
SQRT( REDUCE(x=0.0, a IN COLLECT(r1.rating) | x + a^2) ) as r1_length,
SQRT( REDUCE(y=0.0, b IN COLLECT(r2.rating) | y + b^2) ) as r2_length,
c1,c2
MERGE (c1)-[s:SIMILARITY]-(c2)
SET s.similarity = dot_product / (r1_length * r2_length)MATCH (me:Customer)-[r:SIMILARITY]->(them)
WHERE me.customerID='ANTON'
RETURN me.companyName, them.companyName, r.similarity
ORDER BY r.similarity DESC limit 10太棒了,现在让我们根据这些相似性分数进行推荐。
WITH 1 as neighbours
MATCH (me:Customer)-[:SIMILARITY]->(c:Customer)-[r:RATED]->(p:Product)
WHERE me.customerID = 'ANTON' and NOT ( (me)-[:RATED|PRODUCT|ORDER*1..2]->(p:Product) )
WITH p, COLLECT(r.rating)[0..neighbours] as ratings, collect(c.companyName)[0..neighbours] as customers
WITH p, customers, REDUCE(s=0,i in ratings | s+i) / LENGTH(ratings) as recommendation
ORDER BY recommendation DESC
RETURN p.productName, customers, recommendation LIMIT 10就是这样!使用Neo4j快速简单地实现推荐。
此页面有帮助吗?